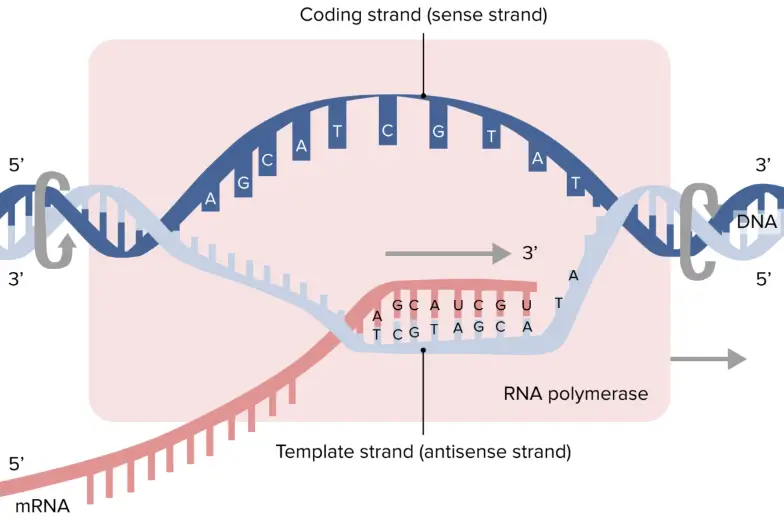
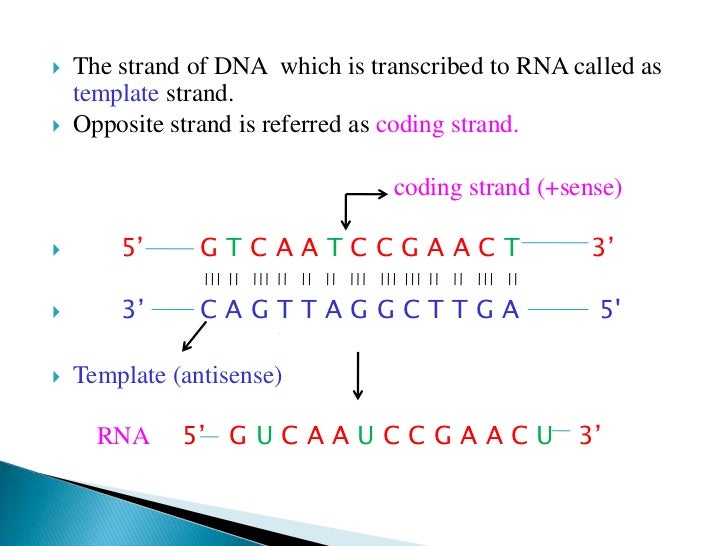
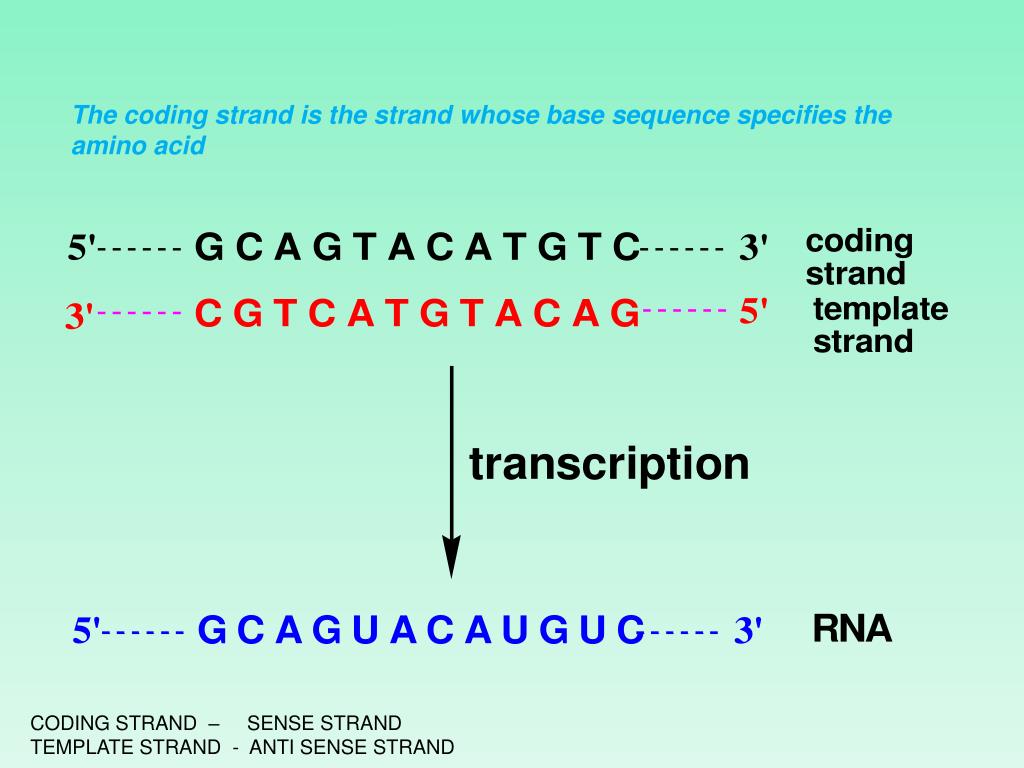
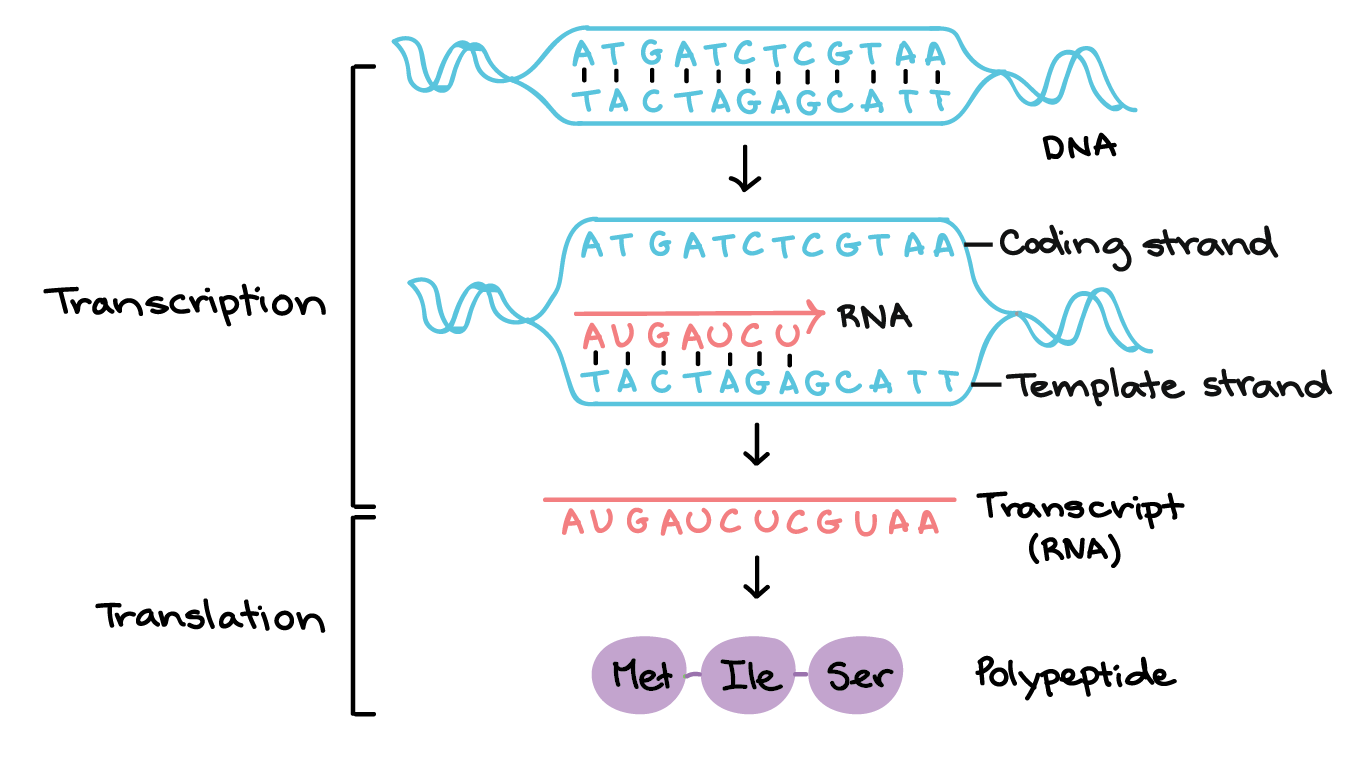
Template Strand And Coding Strand
Template Strand And Coding Strand - Coding strand of dna (sense strand) has the same sequences as transcribed rna, except for having thymine in place of rna’s uracil. Web the coding strand is directly involved in protein synthesis, while the template strand serves as a template for rna synthesis. Coding strand is also called a template strand which gets transcribed to rna. The rna sequence is identical to the coding strand of dna, except that thymine is present in. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. Web the primary difference between coding strand and template strand lies in their nucleotide sequence orientation. When referring to dna transcription, the coding strand (or informational strand) is the dna strand whose base sequence is identical to the base sequence of the rna transcript produced (although with thymine replaced by uracil). This pairing is indispensable for accurate replication and transcription. Web the template strand and the coding strand are the two known strands. Though they are part of the same dna molecule, they have some key differences. Web the template strand and coding strand are two complementary dna strands that play distinct roles in molecular processes such as rna synthesis and protein coding. The other strand, the coding strand, is identical to the rna transcript in sequence, except that it has uracil (u) bases in place of thymine (t) bases. A always pairs with t, and g. Often termed as the antisense strand or minus strand. The coding strand is the strand of dna that has the same sequence as the rna transcript, except that it. Web the coding strand moves in the 5′ to 3′ direction, opposite to the template strand and it. Web the template strand and coding strand are two complementary dna strands that. Template strand is directed in the 5’ to 3’ direction. Here are the key differences between the template strand and the coding strand: The coding strand is the strand of dna that has the same sequence as the rna transcript, except that it. A always pairs with t, and g with c. The coding strand has the same sequence as. The dance of dna the two strands of dna follow strict rules. Web the coding strand is directly involved in protein synthesis, while the template strand serves as a template for rna synthesis. Coding strand of dna (sense strand) has the same sequences as transcribed rna, except for having thymine in place of rna’s uracil. Here are the key differences. Understanding the differences between these two strands is crucial in comprehending the complex processes of dna replication, transcription, and translation. The template strand and the rna produced by the process are complimentary. A always pairs with t, and g with c. Web in the dna molecule, the coding strand and the template strand differ in their bases’ sequence. Considering the. The coding strand or the sense strand corresponds to the same sequence as that of the mrna strand. Coding strand of dna (sense strand) has the same sequences as transcribed rna, except for having thymine in place of rna’s uracil. Web the coding strand and template strand are two complementary strands of dna that play different roles in the process. Coding strand is also called a template strand which gets transcribed to rna. The coding strand has a complementary base sequence to the template strand, except for thymine (t) being replaced by uracil (u) in rna. Though they are part of the same dna molecule, they have some key differences. The coding strand runs in the 5′ to 3′ direction,. Overview of dna structure before delving into the specifics of template and coding strands, let’s briefly outline the structure of dna. The rna sequence is identical to the coding strand of dna, except that thymine is present in. Its counterpart, the antisense strand, guides the creation of a complementary rna strand during transcription. Its sequence is used as a template. The coding strand or the sense strand corresponds to the same sequence as that of the mrna strand. The template strand and the rna produced by the process are complimentary. A always pairs with t, and g with c. Web the template strand of dna is the strand that is used during transcription to produce rna. Web in transcription, a. Web the coding strand and template strand are two complementary strands of dna that play different roles in the process of transcription. Overview of dna structure before delving into the specifics of template and coding strands, let’s briefly outline the structure of dna. The dance of dna the two strands of dna follow strict rules. The rna sequence is identical. Coding strand is also called a template strand which gets transcribed to rna. Its sequence is used as a template during transcription to produce an rna molecule. Web the coding strand moves in the 5′ to 3′ direction, opposite to the template strand and it. Web the coding strand serves as a template for producing complementary rna. Cgatacaaa arrow_forward using the example above, transcribe the following dna strand into mrna and translate that strand into a polypeptide chain, identifying the codons, anticodons, and amino acid sequence. Web in transcription, an rna polymerase uses only one strand of dna, called the template strand, of a gene to catalyze synthesis of a complementary, antiparallel rna strand. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. The coding strand or the sense strand corresponds to the same sequence as that of the mrna strand. Web the template strand of dna is the strand that is used during transcription to produce rna. The coding strand has a complementary base sequence to the template strand, except for thymine (t) being replaced by uracil (u) in rna. 4 given a dna sequence alone, you can annotate open reading frames (orfs) in order to identify the coding strand, with the caveat that not all orfs are genes. When referring to dna transcription, the coding strand (or informational strand) is the dna strand whose base sequence is identical to the base sequence of the rna transcript produced (although with thymine replaced by uracil). Web position of the template and coding strands during transcription. The rna sequence is identical to the coding strand of dna, except that thymine is present in. A always pairs with t, and g with c. The template strand is usually directed 3’ to 5’ in direction. Web this template strand is called the noncoding strand. It is complementary to the coding strand of dna for the target gene. This pairing is indispensable for accurate replication and transcription. Web introduction coding strand vs template strand science encompasses the fundamental components of dna, with the coding strand and template strand playing pivotal roles.Template and coding strand targeting of spacers. A Schematic
DNA Transcription Steps and Mechanism • Microbe Online
Coding Strand of DNA bartleby
Template Strand Vs Coding Strand Understanding The Difference GRAPHICOLD
Transcription
Difference Between Template and Coding Strand Compare the Difference
Difference Between Template and Coding Strand Definition
Difference between Sense Strand and Antisense Strand of DNA Dna
PPT Transcription PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3154392
What strand of DNA is used to make a complementary copy or to make a
Related Post: